You might think that slathering on any sunscreen is enough to protect your skin, but have you ever considered how the UV index should dictate your sunscreen choices? Many people underestimate the importance of the UV index, often treating it as a trivial detail rather than a critical factor in sun protection. In this article, we’ll explore why paying attention to the UV index is essential and how it should influence your sunscreen use.
What is the UV Index?
The UV index is more than just a number; it’s a reflection of how dangerous the sun can be to your skin. The index measures the intensity of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which ranges from 0 to 11+. A higher UV index means stronger UV rays, leading to a higher risk of skin damage. Ignoring this index could mean exposing yourself to severe skin damage without even realizing it.
Why the UV Index Matters
Some argue that just wearing any sunscreen should be enough, regardless of the UV index. However, this approach overlooks the reality that the strength of UV rays can vary drastically day by day. On days with a high UV index, the risk of sunburn is significantly higher, and using the wrong sunscreen might leave you unprotected.
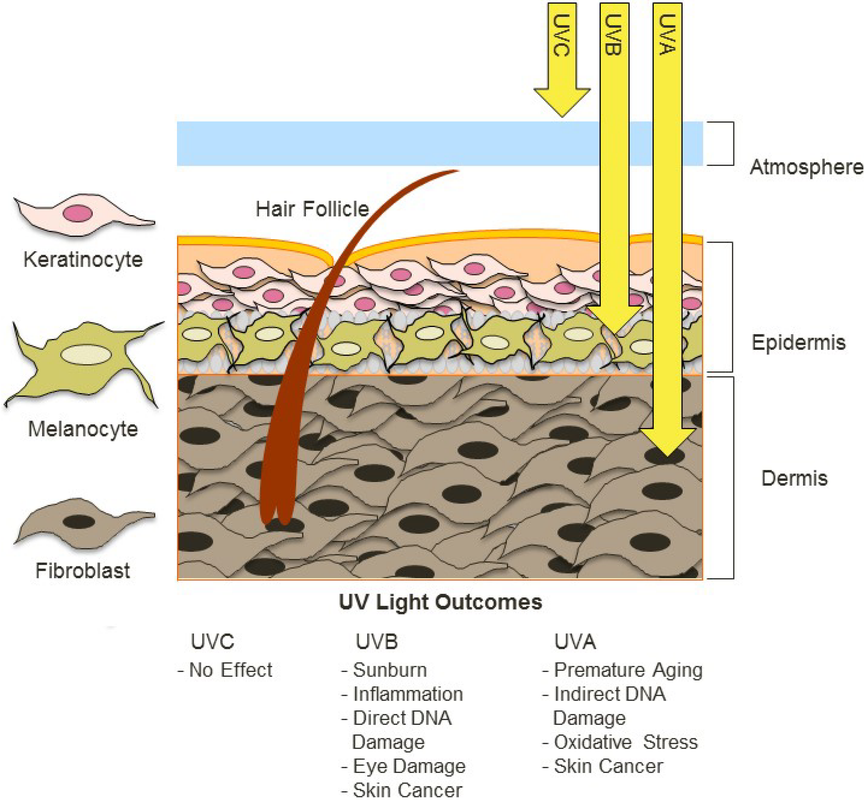
How the UV Index Affects Sunscreen Use
1. Low UV Index (0-2)
Some people believe that on days with a low UV index, sunscreen is unnecessary. While the risk of sunburn is indeed lower, this mindset can be risky. UV radiation is still present, and over time, even low levels of exposure can contribute to skin aging and damage. It’s wiser to apply sunscreen, even on these “safer” days.
2. Moderate UV Index (3-5)
There’s a common misconception that a moderate UV index doesn’t require much attention. However, this level can still lead to sunburn, especially for those with sensitive skin. A sunscreen with at least SPF 30 should be your go-to, despite the moderate label.
3. High UV Index (6-7)
When the UV index is high, some argue that sunscreen alone is enough. But is it really? Given the heightened risk, relying solely on sunscreen might not be sufficient. Combining sunscreen with other protective measures, such as wearing protective clothing and seeking shade, is more prudent.
4. Very High UV Index (8-10)
A very high UV index is where the stakes are high. Some people might think that using a higher SPF sunscreen allows them to stay in the sun longer, but this can be a dangerous assumption. Even with SPF 50+, it’s crucial to limit your sun exposure and reapply sunscreen more frequently.
5. Extreme UV Index (11+)
With an extreme UV index, the argument for maximum sun protection is undeniable. However, some might think that applying the highest SPF available is enough. The truth is, even the best sunscreen can’t fully protect you from such intense rays. Avoiding the sun as much as possible is the safest approach.
The Role of SPF in Sunscreen
Many people assume that a higher SPF means they’re fully protected, no matter how intense the sun is. However, SPF only measures protection against UVB rays, not UVA. Over-reliance on SPF can lead to a false sense of security. It’s critical to understand that no sunscreen can block all UV radiation, and combining sunscreen with other protective strategies is essential.
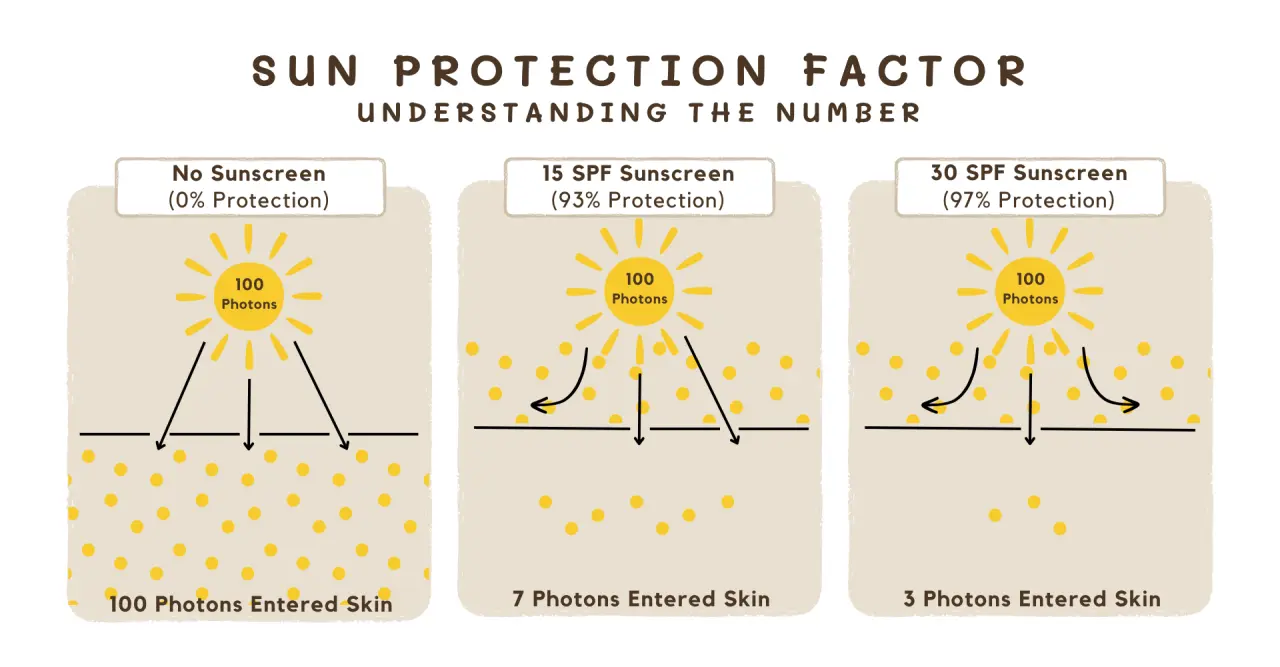
Reapplication is Key
Reapplying sunscreen is often overlooked, yet it’s one of the most important steps in sun protection. Some people believe that a single application in the morning is enough for the entire day, but this is far from the truth. Sunscreen wears off due to factors like sweat, water, and time, making reapplication every two hours a must, regardless of the UV index.
Other Sun Protection Measures
1. Wear Protective Clothing
There’s an argument that sunscreen alone is enough, but why rely on just one method? Protective clothing can significantly reduce UV exposure, acting as a physical barrier between your skin and the sun. It’s an often-overlooked but highly effective strategy.
2. Use Sunglasses
Some might question whether sunglasses are necessary if they’re already wearing sunscreen. The answer is yes, absolutely. UV rays can damage your eyes, leading to cataracts and other issues. Sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays are a small investment for long-term eye health.
3. Seek Shade
It’s easy to think that sunscreen negates the need for shade, but this is a risky assumption. Shade is one of the most effective ways to reduce UV exposure, especially during peak hours when the sun’s rays are strongest. Combining shade with sunscreen offers a double layer of protection.
Understanding Your Skin Type
Your skin type plays a significant role in how you should respond to the UV index. People with fair skin are more vulnerable to sunburn and may need higher SPF products and more frequent reapplication. Ignoring your skin type when choosing sun protection can lead to inadequate protection.
The Importance of Regular Skin Checks
Some might argue that if you’re diligent about sun protection, there’s no need for regular skin checks. However, this complacency can be dangerous. Skin cancer can develop even in areas not typically exposed to the sun. Regular skin checks are vital for catching potential issues early.
Conclusion
The UV index is not just a number to glance at and ignore. It’s a critical tool in determining how much protection your skin needs from the sun’s harmful rays. By understanding and responding appropriately to the UV index, you can significantly reduce your risk of skin damage. Remember, sunscreen is just one piece of the puzzle—combining it with other protective measures is the best way to stay safe under the sun.
FAQs
1. What does a UV index of 5 mean?
A UV index of 5 indicates a moderate risk, so it’s wise to use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and reapply regularly.
2. How often should I reapply sunscreen?
You should reapply every two hours, or more often if you’re swimming or sweating. Assuming one application is enough can lead to sunburn.
3. Can I skip sunscreen on cloudy days?
No, UV rays can penetrate clouds, so it’s important to wear sunscreen even on cloudy days. Skipping it is a risky move.
4. Is higher SPF always better?
Higher SPF offers more protection, but it’s also crucial to reapply and use other sun protection measures. Thinking SPF alone is enough is misleading.
5. Can I rely solely on clothing for sun protection?
Clothing helps, but combining it with sunscreen is the best approach for comprehensive protection.